1. Category:
Permanent magnet synchronous motor:
A type of AC synchronous motor, whose speed is strictly synchronized with the given frequency of the power supply, and the slip is zero.
Asynchronous motor:
It belongs to an AC induction motor. After the stator is connected to AC power, a rotating magnetic field is generated. Electromagnetic induction induces a current in the rotor, which generates electromagnetic torque to rotate the motor. Its speed is always lower than that of the rotating magnetic field, and the slip is not zero.
2. Stator structure:
The stator structure of the permanent magnet synchronous motor is basically the same as that of the asynchronous motor, which plays the role of receiving and outputting electric energy and generating a rotating magnetic field. There is not much difference in their structural forms. The stators of permanent magnet synchronous motors and asynchronous motors are composed of magnetically conductive stator cores, windings, machine bases, end covers, and other components.
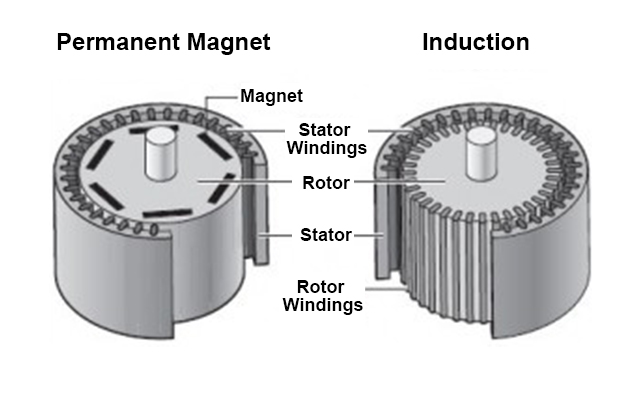
3. Rotor structure:
Asynchronous motor:

induction motor rotor structure
The rotor consists of an iron core and windings, mainly squirrel cage and wound rotors. Aluminum bars are cast in the squirrel-cage rotor. The aluminum strip cutting stator magnetic field drives the rotor to run.
Permanent magnet synchronous motor:
permanent magnet motor rotor
There are permanent magnets embedded in the rotor poles, which are driven to rotate by the rotating magnetic field generated in the stator according to the principle that the same poles repel and the opposite poles attract each other.
The surface or interior of the permanent magnet synchronous motor rotor is embedded with pre-magnetized (magnetized) permanent magnet materials, which can provide the necessary air gap magnetic field for the motor. Adopting this rotor structure can effectively reduce the size of the motor, reduce loss and improve efficiency. In other structures, the motor generates a magnetic field by passing a current through the motor windings.
Such as in ordinary DC motors and synchronous motors, the excitation winding should be specially set to establish the air gap magnetic field. The motor with this structure has a large volume, complex process, high failure rate, severe heat generation, and low efficiency.
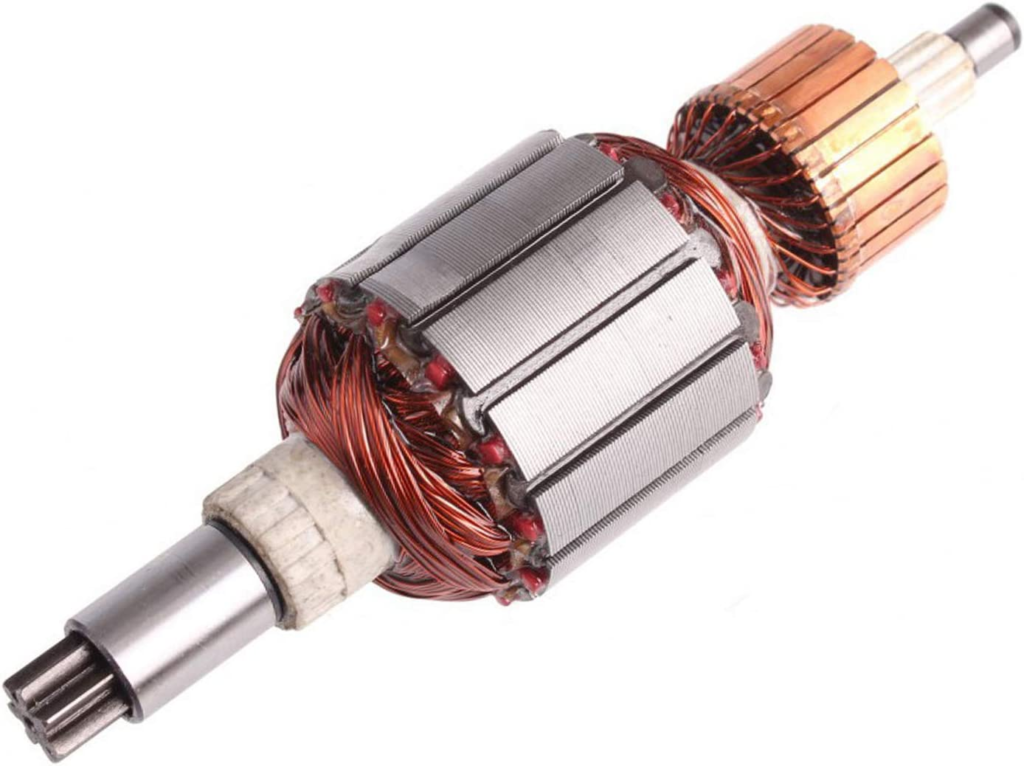

For example, an asynchronous motor needs to absorb inductive reactive current from the grid through the stator winding to establish an air gap magnetic field. Its rotor is cast with aluminum bars. The motor with this structure has a low power factor, reduced efficiency, and large power consumption.
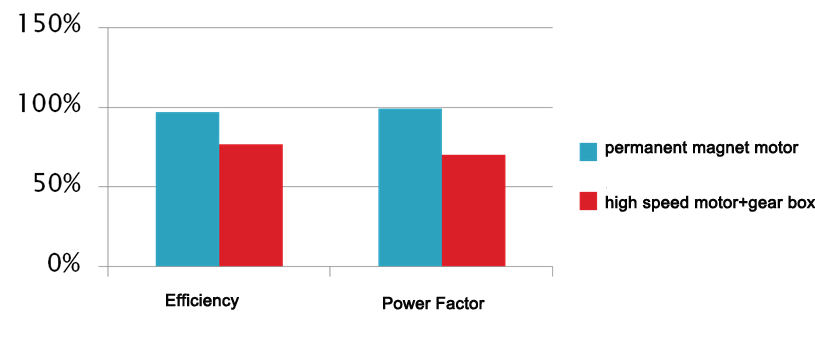
4. Efficiency power factor:
Asynchronous motor:
Due to the need to absorb current excitation from the power grid, a certain amount of energy loss is caused, the reactive current of the motor is large, and the power factor is low;
permanent magnet synchronous motor:
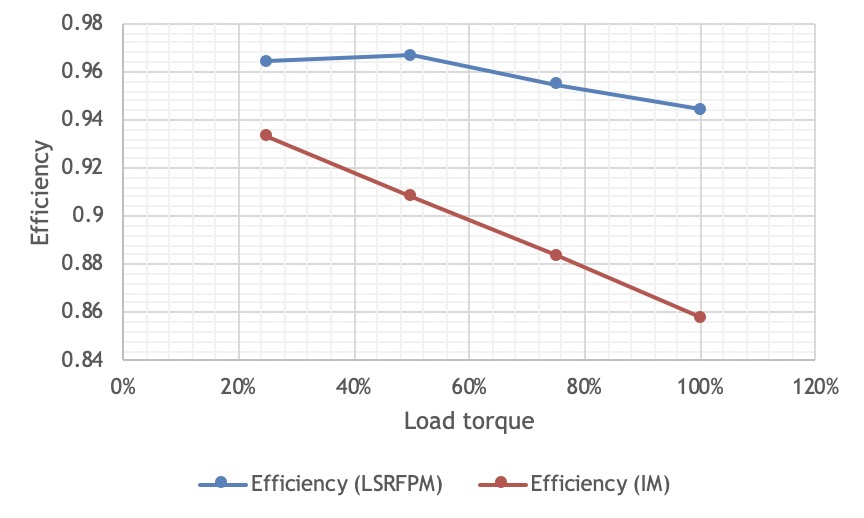
The magnetic field of the permanent magnet synchronous motor is provided by the permanent magnet, the rotor does not need excitation current, and the motor efficiency is improved. Compared with the asynchronous motor, any speed point can save electric energy, especially when the speed is low. This advantage is particularly obvious. The permanent magnet synchronous motor can maintain extremely high efficiency and power factor in the entire speed range.
5. Volume and weight:
The use of high-performance permanent magnet materials makes the air gap magnetic field of permanent magnet synchronous motors larger than that of asynchronous motors. Compared with asynchronous motors, permanent magnet synchronous motors are smaller in volume and weight. It will be one or two frame sizes lower than the asynchronous motor, and the permanent magnet synchronous motor has low loss, high efficiency, and flexible shape and size. (The low-speed direct-drive permanent magnet motor replaces the reducer and increases the torque, and its size comparison should be compared with the appearance size of the asynchronous motor + reducer)
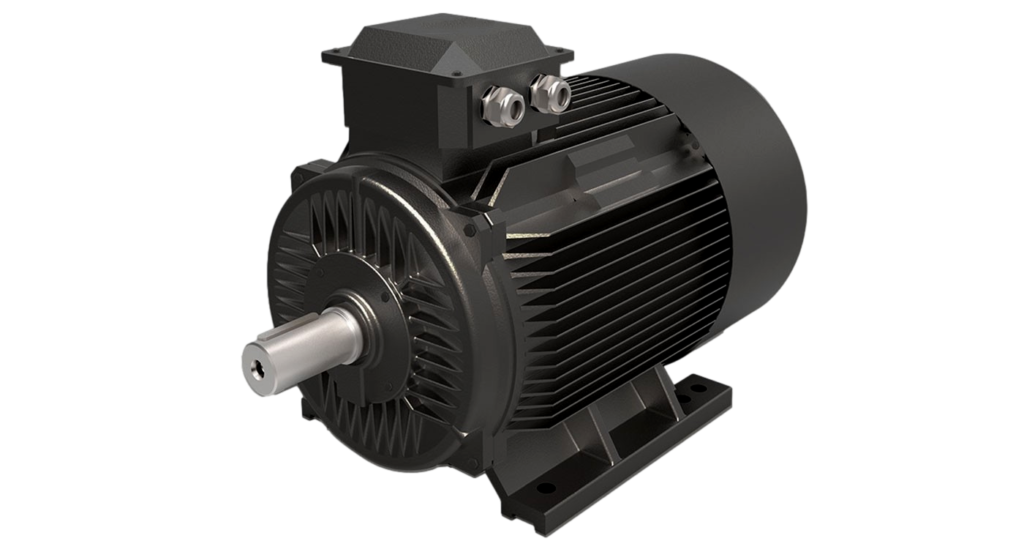

permanent magnet motor
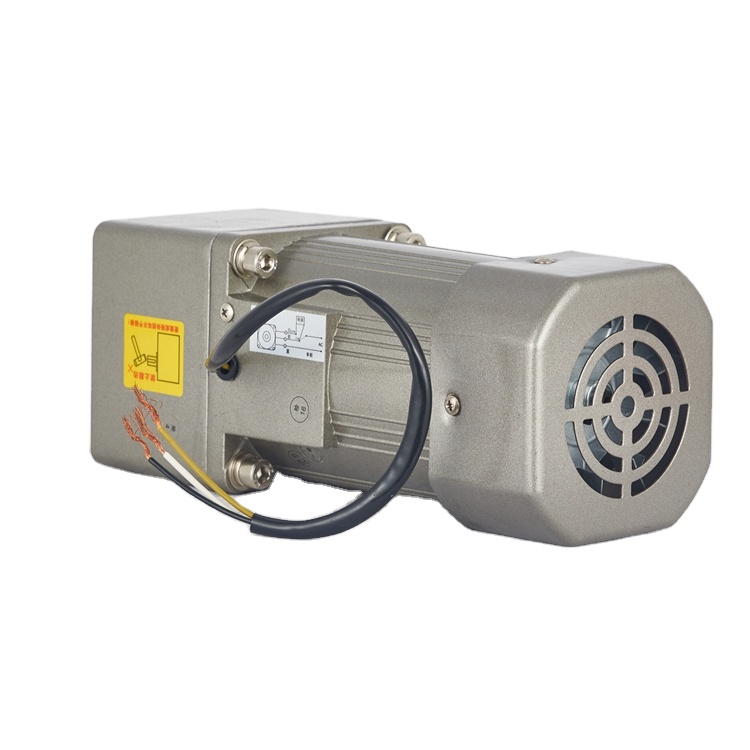

asynchronous motor+ reducer
6. Motor starting current:
Asynchronous motor:
It is directly started by power frequency electricity, and the starting current is large, which can reach 5 to 7 times the rated current, which has a great impact on the power grid in an instant. The large starting current leads to an increase in the leakage impedance voltage drop of the stator winding, and the starting torque is small, making it impossible to achieve heavy-duty starting. Even if a frequency converter is used, it can only be started within the rated output current range.
Permanent magnet synchronous motor:
Driven by a dedicated controller, it lacks the rated output requirements of the reducer, the actual starting current is small, the current gradually increases according to the load, and the starting torque is large. Under the same line capacity, it is easier to achieve heavy-duty starting by using a permanent magnet synchronous motor.
7. Power factor:
The power factor of the asynchronous motor is low, and it needs to absorb a large amount of reactive current from the power grid, resulting in a large amount of reactive current in the power transmission and transformation equipment and power generation equipment of the power grid, which in turn reduces the quality factor of the power grid and aggravates the load on the power grid, power transmission, and transformation equipment and power generation equipment. equipment load. The starting current of the asynchronous motor is large, which will cause a short-term impact on the power grid, and long-term use will cause certain damage to power grid equipment and transformers. It is necessary to add power compensation units for reactive power compensation to ensure the quality of the power grid and increase the cost of equipment use.
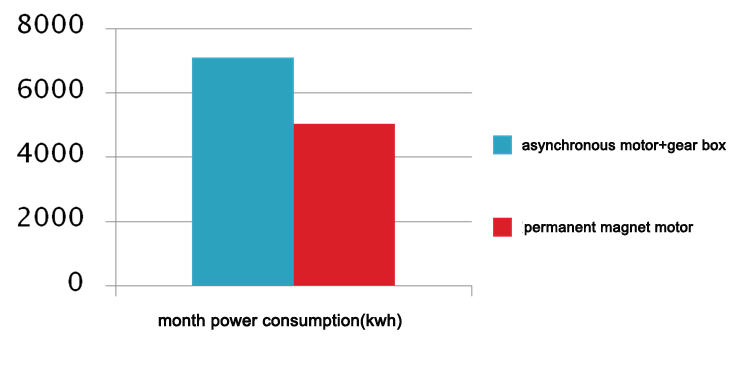
There is no induction current in the rotor of the permanent magnet synchronous motor, and the power factor of the motor is high, which improves the quality factor of the power grid, and no need to install a compensator. At the same time, due to the high efficiency and high power factor of the permanent magnet motor, the capacity of the power supply and transformer supporting the motor can be lower than that of the asynchronous motor, and the specifications of other auxiliary facilities such as switches and cables can be smaller, and the corresponding system cost is lower.
8. Maintenance:
The permanent magnet synchronous motor directly drives the equipment. Due to the cancellation of the reducer, the output speed of the motor is low, the mechanical noise is low, the mechanical vibration is small, the failure rate is low, and the entire drive system is almost maintenance-free.
The structure of the asynchronous motor + gearbox will generate vibration, heat, high failure rate, large consumption of lubricating oil, and high cost of manual maintenance; it will cause certain downtime losses.